Corneal Transplant
"Lamellar corneal transplantation is a major advance over conventional transplantation that involves replacing the entire cornea."
DR. MIGUEL NAVEIRAS SPECIALIST. OPHTHALMOLOGY DEPARTMENT

Corneal transplant or keratoplasty is a surgical technique that consists of replacing damaged tissue with that of a healthy donor. It allows to recover the transparency of the eye and, with it, the visual function.
The cornea is a transparent and curved tissue located in the front part of the eye, which acts as a lens to focus the images of the retina.
As it is located outside, it often suffers injuries caused by external agents, such as trauma or infections that damage its transparency and affect vision.

When is a corneal transplant indicated?
The cornea transplant or keratoplasty is performed to achieve a transparent cornea, which is functional and guarantees vision.
It is indicated in patients, fundamentally, with keratoconus or patients who have suffered a trauma that has damaged all or part of the cornea.
Most frequent indications of this treatment:
- Keratoconus (thinning of the cornea).
- Scars or serious eye infections.
Do you have any of these diseases?
You may need a corneal transplant
 Lamellar Corneal Transplant
Lamellar Corneal Transplant
EN MADRID
What Lamellar Corneal Transplant Involves
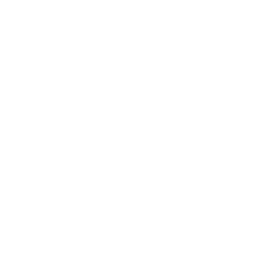
The lamellar corneal transplant is a minimally invasive surgery that involves replacing only the affected layers while preserving the rest of the healthy tissue.
It represents a major advancement compared to conventional transplantation, which requires replacing the entire cornea.
A lower risk of complications and rejection, along with improved quality of life, are some of the advantages of minimally invasive corneal transplants.
Most Common Indications for Lamellar Corneal Transplant
- Fuchs endothelial dystrophy.
- Keratoconus.
- Herpetic leukoma.
- Bullous keratopathy.
- Acanthamoeba leukoma.
- Bacterial leukoma.
- Traumatic leukoma.
- Stromal dystrophy.
- Posterior polymorphous dystrophy.
- Corneal edema due to anterior chamber lens.

“Entre las principales ventajas este tipo de trasplante destacan el menor riesgo de complicaciones y la menor tasa de rechazo, así como una mejora drástica en la calidad de vida”.
DR. MIGUEL NAVEIRAS
Departamento de Oftalmología. Madrid
Lamellar Transplant Technique: DMEK
With a one-day hospital stay, this technique is recommended for patients with Fuchs endothelial dystrophy or bullous keratopathy.
To perform it, two attached parts are removed together: the posterior layer (the damaged endothelium) and its supporting membrane (Descemet’s membrane), removing only the diseased cellular tissue.
These transplants usually take between two and three hours (depending on the case, general anesthesia or sedation is used, but the patient is always asleep).
Lamellar Transplant Technique: DALK
With a one-day hospital stay, this technique is especially indicated for patients with leukoma or severe keratoconus (corneal thinning).
To perform it, the front layers of the cornea (stroma and epithelium) are removed while preserving the innermost layer (the endothelium).
Finally, it is sutured with fine stitches that are barely noticeable.
Lamellar Transplant Technique: DALK
With a one-day hospital stay, this technique is especially indicated for patients with leukoma or severe keratoconus (corneal thinning).
To perform it, the front layers of the cornea (stroma and epithelium) are removed while preserving the innermost layer (the endothelium).
Finally, it is sutured with fine stitches that are barely noticeable.

Learn more about corneal transplantation
Most patients do not suffer pain in the operated eye, although some discomfort may occur. The eye of the transplanted cornea requires treatment with eye drops and, occasionally, general treatment. It may even need immunosuppressive medication. The visual recovery is progressive.
The postoperative follow-up lasts several months and a careful control is necessary on the part of the professionals who take care of him to avoid the complications in the long term.
The patient may require optical correction -glasses or contact lenses- to achieve the best possible vision.
Keratoplasty can be performed at the same time as cataract or glaucoma surgery. However, in these cases visual recovery is more complicated.
The Department of Ophthalmology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
Equipped with the latest technology, the Department of Ophthalmology has the necessary equipment, both technical and human, to offer comprehensive and specific assistance to each patient.
We are one of the few centers that have a microsurgery laboratory for the improvement of clinical practice.
Organized in specialized units
- Cornea and eye surface
- Retina
- General Ophthalmology
- Refraction defects
- Oculoplastic
- Pediatric ophthalmology

Why at the Clinica?
- More than 30 years of experience.
- Experts in the diagnosis and treatment of ocular pathologies.
- With the security and guarantee of a prestigious hospital.