Crohn's Disease
"Infliximab, the first authorized anti-TNF antibody, acts by neutralizing the TNF produced in the patient, and is indicated in fistulizing Crohn's disease that does not respond to treatment with antibiotics and/or immunosuppressants".
DR. RAMÓN ANGÓS
SPECIALIST. DIGESTIVE DEPARTMENT

Crohn's disease is a chronic, autoimmune inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract that evolves in a recurrent manner with outbreaks.
Of unknown cause, among its main symptoms are abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, weight loss, rectal bleeding, etc.
Crohn's disease can affect from the mouth to the anus. The most frequent location is the terminal ileum (most distal portion of the small intestine).
It can present manifestations outside the digestive system as in joints, skin, liver, eyes...
It usually occurs in young people (2nd-3rd decade of life) although it can manifest itself at any age.

What are the symptoms of Crohn's disease?
The symptoms depend on the anatomical location and the severity of the inflammation.
The main symptom of Crohn's disease is diarrhea and abdominal pain usually located on the right side. It may be accompanied by fever.
If there is any point with difficulty in passing, nausea and vomiting would be associated.
The perineal affectation is habitual being able to exist communication between intestinal loops or between intestine and other viscera (fistulas).
The most common symptoms are:
- Diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain.
- Fever.
- Perineal affectation.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have Crohn's disease
What are the causes of Crohn's disease?
The cause of this disease is not known, but everything suggests that there are multiple factors involved in its origin.
There are many hypotheses, but the most current one is that there is an alteration in the immune system to food or bacterial antigens.
Other theories establish an infectious process as the trigger of the disease, with several germs being involved.
What is the prognosis of Crohn's disease?
Since no drug is available at the moment that will prevent recurrences, the prognosis is uncertain and individual. In general, the quality of life between outbreaks is good and normal life is possible.
The prognosis is generally related to the time of evolution of the disease since the diagnosis, the extension of the disease, the severity of the outbreaks, the existence or not of complications and the history of surgical treatment.
A special mention is made of the possibility of malignancy in the course of this disease. There is an increased risk of tumor, especially of the colon, compared to the general population. For this reason, early diagnosis is important and an annual endoscopic follow-up is recommended after 10 years of diagnosis.
How is Crohn's disease diagnosed?
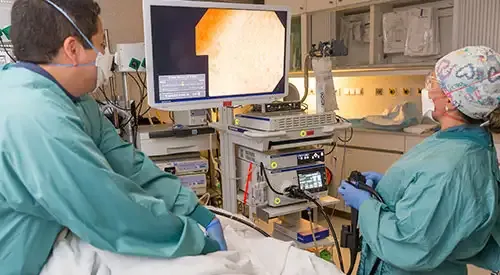
The diagnosis of Crohn's disease is made with clinical suspicion and compatible radiological, endoscopic and histological (biopsy) findings.
The analysis is altered in the acute phases of the disease with elevated sedimentation rate (ESR and C-reactive protein), increased white blood cell and platelet counts.
Radiological studies (TAC, ultrasound, intestinal transit) show the possible complications of these entities (abscesses, fistulas, stenosis...).
The scan with marked leukocytes can allow the extension of the inflammation to be assessed.
At the time of the appearance of symptoms, the doctor must differentiate from other diseases that can also occur with outbreaks of diarrhea, bloody abdominal pain and / or fever.
How is Crohn's disease treated?
Steroids, 5-ASA, antibiotics or immunosuppressants can be used in outbreaks. There are other newer treatments based on the alteration of the immune system such as anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies.
In the remission phase it should be tried to remove, although it is not always possible, the intake of steroids leaving the maintenance 5-ASA.
Surgery has its role above all as a treatment for complications (toxic megacolon, perforation, abscesses, stenotic areas, fistulas, malignancy...).
The Department of Digestive
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Digestive Department of the Clinica Universidad de Navarra is composed of a multidisciplinary team of specialists who are experts in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract.
Our objective is that each diagnosis be carefully established and the treatment plan adjusted to each patient.

Why at the Clinica?
- Medical specialists who are national references.
- Specialized nursing team.
- Endoscopy Unit and High Risk Digestive Tumor Prevention and Consultation Unit to offer the best care to our patients.















