Gynecological bleeding
"Any woman who experiences abnormal uterine bleeding should be evaluated in a physician's office".
DR. MARÍA AUBÁ
SPECIALIST. GYNAECOLOGY AND OBSTETRICS DEPARTMENT

Abnormal uterine bleeding is defined as when either the frequency or the amount of uterine bleeding differs from that mentioned above. Or uterine bleeding occurs unrelated to the menstrual cycle.
Menstruation is considered normal when uterine bleeding occurs between every 25 and 35 days and is not excessive. The normal duration of bleeding is between 2 and 7 days.
Any woman who experiences abnormal uterine bleeding should be evaluated at a physician's office, including a physical examination and possibly an endometrial biopsy.

What are the symptoms of uterine bleeding?
Bleeding is considered abnormal when it occurs in the following situations:
- Bleeding between periods.
- Bleeding after sex.
- Blood spots at any time during the menstrual cycle.
- Bleeding more heavily or for more days than normal.
- Bleeding after menopause.
- Absent periods for 3 to 6 months (amenorrhea) are also abnormal
Abnormal uterine bleeding may be due to structural abnormalities of the uterus or what is called dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Structural abnormalities include benign lesions such as endometrial polyps, fibroids or uterine fibroids and adenomyosis. It can also be the manifestation of endometrial cancer.
At other times it may be due to lesions at the level of the cervix or vagina, whether benign or cancerous, chronic infections of the endometrium (endometritis) or the use of intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Other causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, not directly related to structural abnormalities, may include the use of medications that affect the normal production of estrogen and progesterone; chronic medical diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, diseases of the liver, kidney, thyroid or adrenal glands, and problems with blood clotting.
Physical or emotional stress can also induce the appearance of abnormal uterine bleeding.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have uterine bleeding
How is uterine bleeding diagnosed?
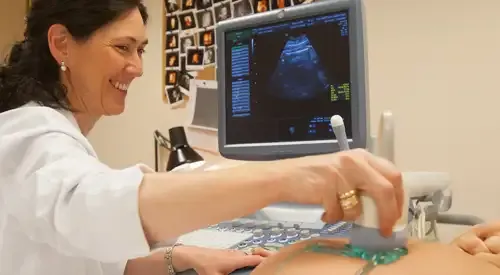
Among the diagnostic procedures that should be performed to determine the cause of such bleeding, we would place, in the first place, the physical examination.
Ultrasound is undoubtedly the most widely used diagnostic imaging technique in the evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding. It allows the study of the uterus and the ovaries. It allows to identify in which woman the endometrial biopsy could be avoided since a normal ultrasound significantly reduces the possibility of an endometrial lesion. This will avoid unnecessary biopsies.
Hysteroscopy is also a very useful diagnostic procedure in the diagnosis of abnormal uterine bleeding. It allows the endometrial biopsy to be performed in a way that is more directed at the lesion itself, thus reducing false negatives.
Under certain circumstances, it may be advisable to perform a uterine curettage. This normally has to be done under general anaesthesia, and in addition to providing diagnostic information, it will be therapeutic on some occasions.
On the other hand, there are causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in relation to chronic diseases or coagulation alterations, as well as anovulation. For this reason, it may be advisable to perform a series of blood tests to rule out alterations in those organs that may induce the appearance of such abnormal bleeding.
How is uterine bleeding treated?
Individualized treatment according to the specific cause of the abnormal bleeding is highly recommended. Age and whether the woman wants to have children are also important considerations.
In the case of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, that is to say, that due to anovulation, the treatment will be fundamentally medical, by taking drugs (either taken orally or used in the form of an intrauterine device) that restore ovulation or allow control of the bleeding.
If these treatments fail, a useful alternative is endometrial ablation, that is, the exeresis of most of the endometrial tissue, which would allow a decrease in the amount of bleeding. It is performed hysteroscopically under general anesthesia. It is important to exclude serious endometrial lesions, mainly endometrial cancer, before performing this procedure.
The use of Caviterm, which produces endometrial atrophy by using high temperature distilled water instilled by an instrument specifically designed for this purpose, has also been recently described. This treatment should be reserved for those patients who do not have fertility desires. It is performed hysteroscopically under general anesthesia. It is important to exclude serious endometrial lesions, mainly endometrial cancer, before performing this procedure.
In the case of chronic diseases that induce abnormal uterine bleeding, the therapeutic approach should be directed primarily to the treatment of that disease, with measures similar to those described above being helpful.
Structural abnormalities of the uterus or endometrium will have a specific treatment, fundamentally of a surgical type, either using hysteroscopy, such as the exeresis of myomas and polyps; or by means of open surgery (laparotomy), with the possibility of only removing the myoma, if this is the cause of the bleeding (which is called myomectomy); or, in extreme circumstances, the exeresis of the uterus (hysterectomy).
The Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
Comprehensive care that includes a wide range of consultation and treatment options from regular preventive screening to the most advanced diagnostic and treatment options for obstetric and gynecological problems at all ages.
The department also offers routine pregnancy monitoring that includes a variety of diagnostic and screening procedures to identify potential problems of the fetus as well as its proper growth and development.
Diseases we treat
- Gynecological Cancer
- Prenatal diagnosis
- Endometriosis
- Urinary and fecal incontinence
- Masas anexiales
- Menopause
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Uterine Myomas

Why at the Clinica?
- Highly specialized team of doctors, nurses and midwives.
- Reproduction and Fertility Unit.
- Pregnancy follow-up with a personalized delivery.
- All the comfort, with the guarantee and safety of a hospital with the most advanced equipment.

























