Groin Hernia
"The definitive treatment for inguinal hernia is surgical".
DR. CARLOS SÁNCHEZ JUSTICIA
SPECIALIST. GENERAL AND DIGESTIVE SURGERY DEPARTMENT

What is inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia is the protrusion or leakage of the contents of a cavity to the outside, usually through a natural orifice or an area of weakness in the wall that contains it.
About 75% of all hernias occur in the inguinal region, so that by inguinal hernia is understood the exit to the outside of the contents of the abdominal cavity (usually bowel loops) at the level of the inguinal region.

What are the symptoms of inguinal hernia?
Usually the patient who presents an inguinal hernia refers a lump or swelling in the inguinal region. Sometimes it is associated with mild pain or vague discomfort, which is usually accentuated by exertion.
In case of the appearance of great intensity pain, the appearance of a complication must be ruled out: hernia incarceration. This consists of the impossibility of returning the contents of the hernia to the abdominal cavity by compression at the level of the exit orifice.
If, in addition, the blood circulation of the intestine is compromised, then it is a strangulated hernia and in the face of such symptoms it is advisable to go quickly to a medical center to evaluate urgent surgical treatment, given the risk of injury to the herniated intestinal loop.
It is also possible the appearance of inguinal hernias that do not manifest as lumps at this level but only with a clinic of vague and imprecise discomfort especially when walking or making efforts.
What are the most common symptoms?
- Lump in the groin region.
- Mild pain.
- Intense pain during the hernia's evolution.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have an inguinal hernia
What are the causes of inguinal hernia?
Traditionally the factors that lead to the development of hernias are divided into two categories:
- Defect of congenital origin.
- Acquired defects.
In the first of these cases, the persistence of the duct through which the testicle descends in the male from the abdominal cavity to the scrotum (or the round ligament in the female), due to a lack of closure of the same, makes it possible to herniate loops of intestine from the abdominal cavity at this level. Approximately 5 out of 100 children present inguinal hernias.
On the other hand, significant efforts during defecation, coughing, lifting heavy objects, etc., have been implicated as causal factors of trauma and weakening of the inguinal wall and therefore of the formation of hernias.
People who have any of the following risk factors are more likely to develop a hernia: family history of hernias, cystic fibrosis, cryptorchidism, overweight, chronic cough, chronic constipation, strained bowel movements, enlarged prostate.
Other types of inguinal hernia
Similar to the case of inguinal hernias, umbilical hernia consists of the exit of intestinal contents through the abnormally enlarged umbilical orifice. The clinic that produces this type of hernia consists of the appearance of a lump at the umbilical level and the treatment is also surgical, proceeding to the closure of the defect directly or through the placement of mesh when the amplitude of the same is large.
By incisional hernia or eventration is known to the herniation of intestinal content through a failure in a surgical incision previously made for another reason.
The treatment of analogous form to the umbilical one, consists of the direct closing of the defect, or by means of the positioning of a mesh or prothesis, based on the diameter of the same one, because if this one is great the accomplishment of a direct closing would imply an excessive tension in the line of suture increasing the risk of reappearance of the hernia.
How is inguinal hernia diagnosed?
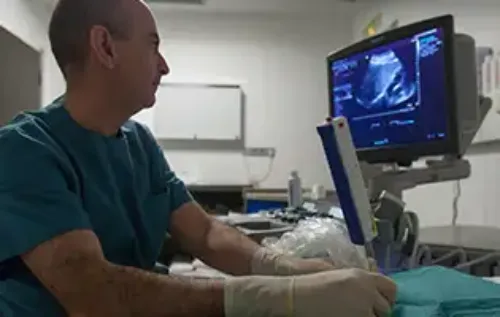
The diagnosis of inguinal hernia lies in the verification of the existence of protrusion at the hernia level, especially when performing abdominal stress maneuvers, coughing, etc., so that, most of the time, the physical examination reveals the presence of the hernia.
Ultrasound and CT scans are useful for detecting small hernias. In some cases, the hernia reaches a large size, being apparent to the naked eye.
The differential diagnosis must be made especially with varicocele and hydrocele.
How is inguinal hernia treated?
The definitive treatment of the inguinal hernia is the surgical one and consists of the reintroduction of the abdominal content and repair or reinforcement of the inguinal wall.
To perform this repair or herniorrhaphy, there are several techniques that range from the use of their own tissues (muscles, fascias, etc.) to restore the integrity of the abdominal wall, to the use of artificial limbs or mesh that play this role.
One of the latest advances in the surgical treatment of inguinal hernias consists of repairing them by laparoscopy, especially indicated in those hernias that have already been operated on previously and have reappeared or those that initially manifest themselves on both sides.
The Department of General Surgery
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of General and Digestive Surgery is made up of specialists dedicated to the surgical treatment of endocrine, breast, gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, pancreatic, colorectal and abdominal wall diseases, with special dedication to oncological surgery.
The application of laparoscopic surgery in the interventions reduces the hospital stay, the post-operative discomfort and shortens the patient's recovery.
We have a great experience in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, of the adrenal gland, liver and pancreas, as well as in obesity surgery.
Treatments we perform
- Colorectal surgery.
- Breast surgery.
- Surgery of the hemorrhoids.
- Pelvic floor surgery.
- Endocrine and obesity surgery.
- Esophageal and gastrointestinal surgery.
- Hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery.
- Abdominal wall surgery.
- Liver transplant.

Why at the Clinica?
- Center of Excellence in Obesity Surgery by the International Federation for Bariatric Surgery.
- 90% survival rate in liver transplants.
- We are the private hospital with the largest technological equipment.

















